Net Positive Suction Head (NPSH)
Cavitation occurs in a fluid when the absolute pressure drops below the vapor pressure of the fluid, resulting in cavitation (formation and collapse of small vapor pockets). The most common place where this occurs in water and wastewater systems is at the suction side of a pump. The head needed to prevent cavitation is called the Net Positive Suction Head required (NPSHr). This value is compared with the Net Positive Suction Head Available (NPSHa) at the pump. If NPSHa > NPSHr, then cavitation damage is unlikely to occur.
The software calculates the NPSHa and can compare it with the NPSHr which the user obtains from the pump specifications.
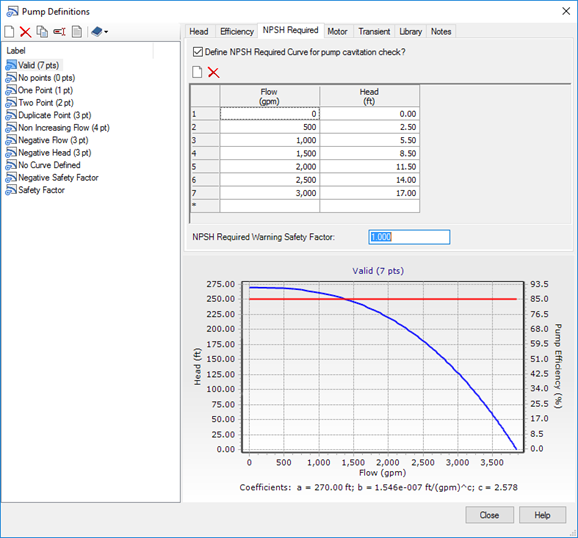
NPSHr Data Entry
The NPSHr is a function of pump flow and is usually available as a curve from the pump manufacturer. The user enters this data in a table by clicking Pump Definition on the Home or Components tabs, picking the pump of interest and selecting the NPSH tab.
To start entering data, the user checks the box "Define NPSH Required Curve for pump cavitation check?" If box is not checked, NPSH results for that pump are not calculated.
The NPSHr curve must be upward sloping. The tabular data must have at least two points.
The user may want to provide a safety factor above that provided in the manufacturer's curve. Click the box labelled "NPSH Required Warning Safety Factor" and enter a multiplier to be applied to the NPSHr.
NPSHa Calculations
Available NPSH is calculated at every time step for every pump using the equation below:
NPSHa = Hb + HGL - Elev - Hvap - Loss
Where: Hb = barometric pressure, ft
HGL = hydraulic grade at pump suction, ft
Elev = elevation of pump impeller
Hvap = vapor pressure (absolute) of water at temperature, ft
Loss = head loss between inlet of pump and impeller (Usually negligible), ft
Barometric pressure can be specified in the field [ exact name] and vapor pressure can be specified in the field [exact name] in the calculation options. The default values are [values].
Results
NPSHa is calculated in all model runs and displayed in the results field "NPSH (Available)".
If the user has specified an NPSHr curve, the model also calculates NPSHr at each time step. There are two additional properties.
These include the safety factor specified by the user.
If NPSHa does not exceed NPSHr at all times, a good way to review the results is to graph NPSHa and NPSHr along with flow to understand the conditions under which cavitation can occur.